Filtered results
-
Study on Economics of Coal-fired Power Generation Projects in China Report
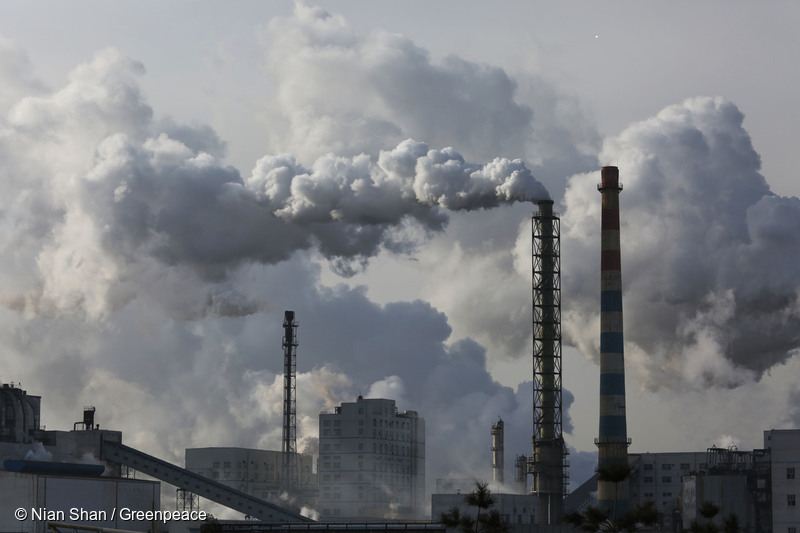
After analyzing the thermal-power (coal-power) related phemonenon and data of the power sector in 2015, the mismatching of use and resources remains complex. With a 2.3% annual drop in thermal power generation and only 0.5% growth in total electricity consumption, the addition of installed capacity of coal-fired plants is incompatible with demand at 52,000 megawatts…
-
China’s air pollution problem is heading west
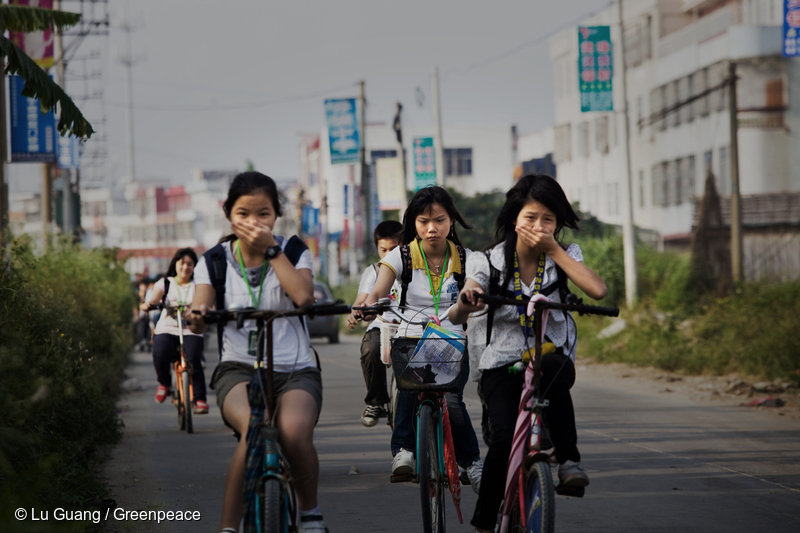
The data is in, and at first glance it looks like good news. China’s air quality has improved overall, but much of its less developed middle and western cities have seen marked increases in PM2.5 levels.
-
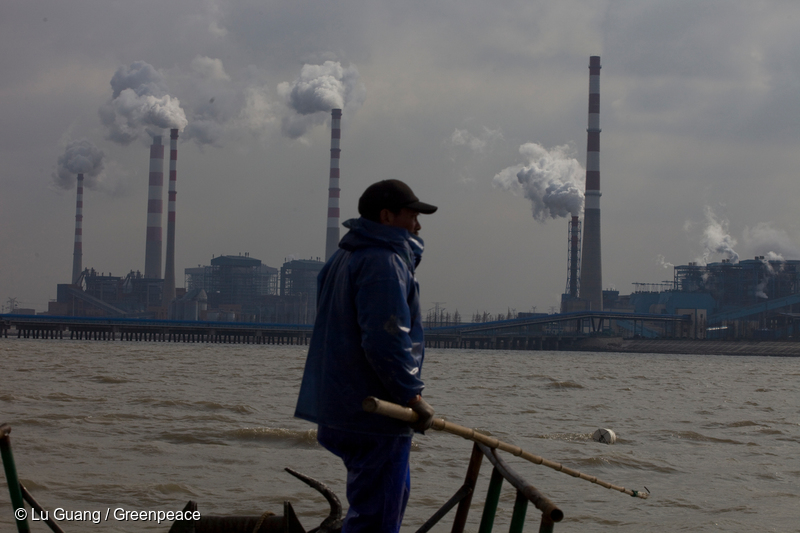
As eastern China’s air quality improves rapidly, 69 cities in central and western China see air quality deteriorating – Greenpeace
Beijing, 20 April, 2016 – Greenpeace East Asia’s city rankings for the first quarter of 2016 show significant improvements in average air quality in 362 cities across the country. The improvements are particularly rapid in eastern China’s three ‘key regions’. [1] However, air quality in more than 85% of cities failed to meet national standards.…
-
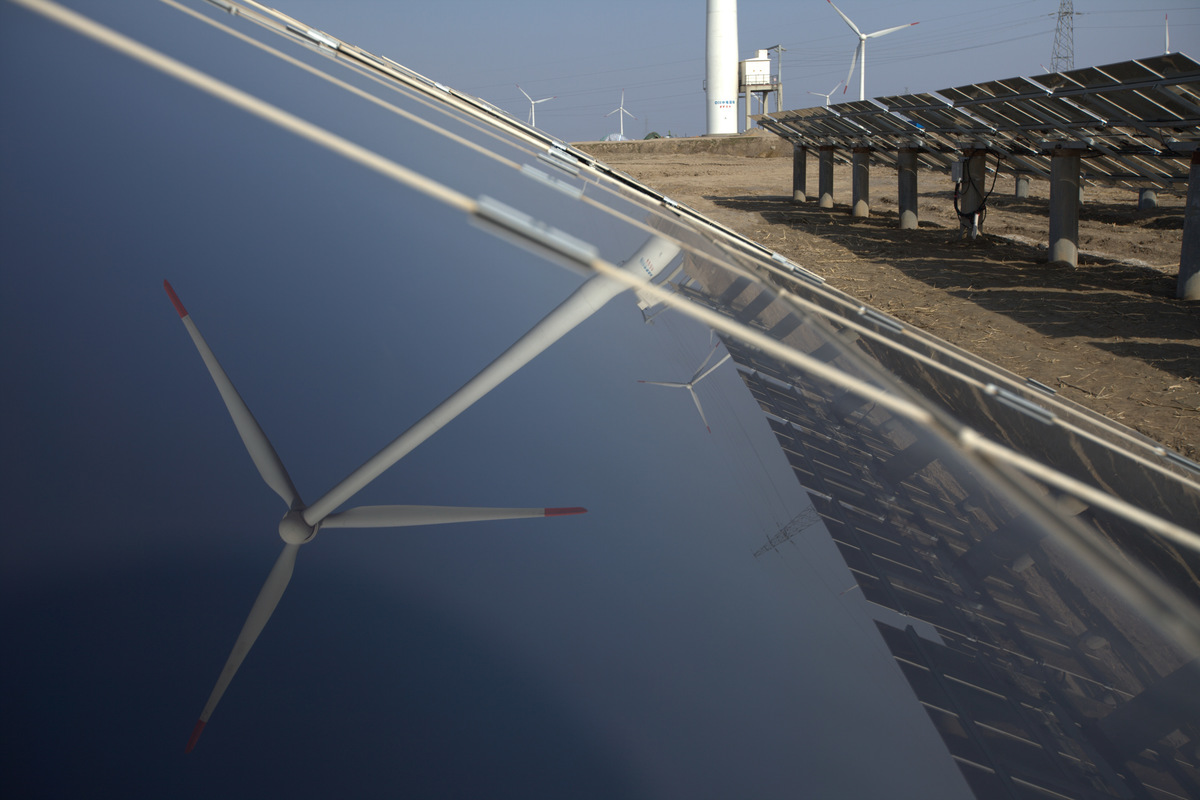
Data shows China’s economy is breaking free from coal – Greenpeace
Beijing, 15 April, 2016 - A trove of data on economic performance in the first quarter of 2016, released by China’s National Bureau of Statistics this morning, shows that while China’s overall economy saw some improvement, coal use and CO2 continue to fall. Electricity consumption grew 3% year on year, but growth in non-fossil energy…
-
Boom and Bust 2016
The world has too many coal-fired power plants, yet the power industry continues to build more. While the amount of electricity generated from coal has declined for two years in a row, the industry has ignored this trend and continues to build new coal-fired generating plants at a rapid pace, creating an increasingly severe capacity…
-
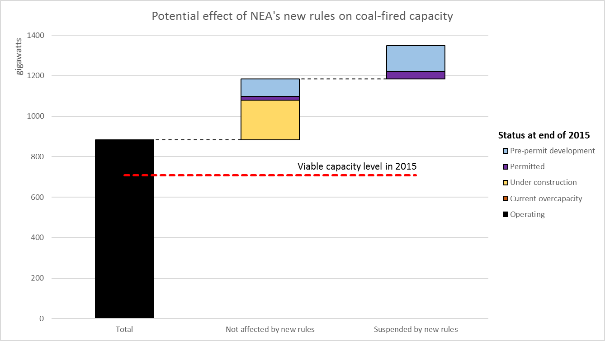
China begins to suspend coal-fired power plant approvals, Greenpeace response
Beijing, 24 March, 2016 - Chinese media today reported that the country’s National Energy Administration (NEA) has ordered 13 provincial governments to suspend approvals of new coal-fired power plant projects until the end of 2017. [1] Another group of 15 provinces has been ordered to delay new construction of projects that have already been approved.…
-
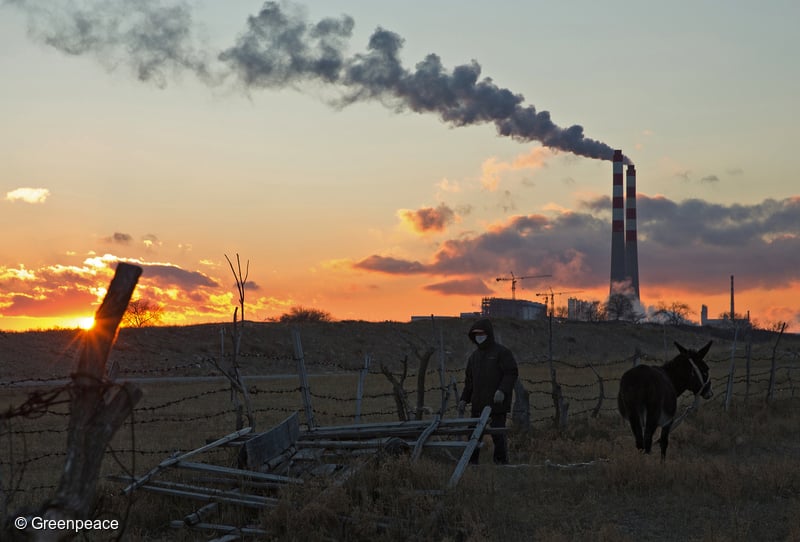
45% of China’s coal-fired power plants in areas of ‘water over-withdrawal’, Greenpeace
Beijing, 22 March, 2016 – 45% of coal-fired power plants in China are located in areas of ‘water over-withdrawal’, a ground-breaking Greenpeace study of the coal industry’s impact on the global water crisis shows. Every year these power plants consume quantities of water equivalent to the basic requirements of 186 million people. Moreover, 48% of…
-
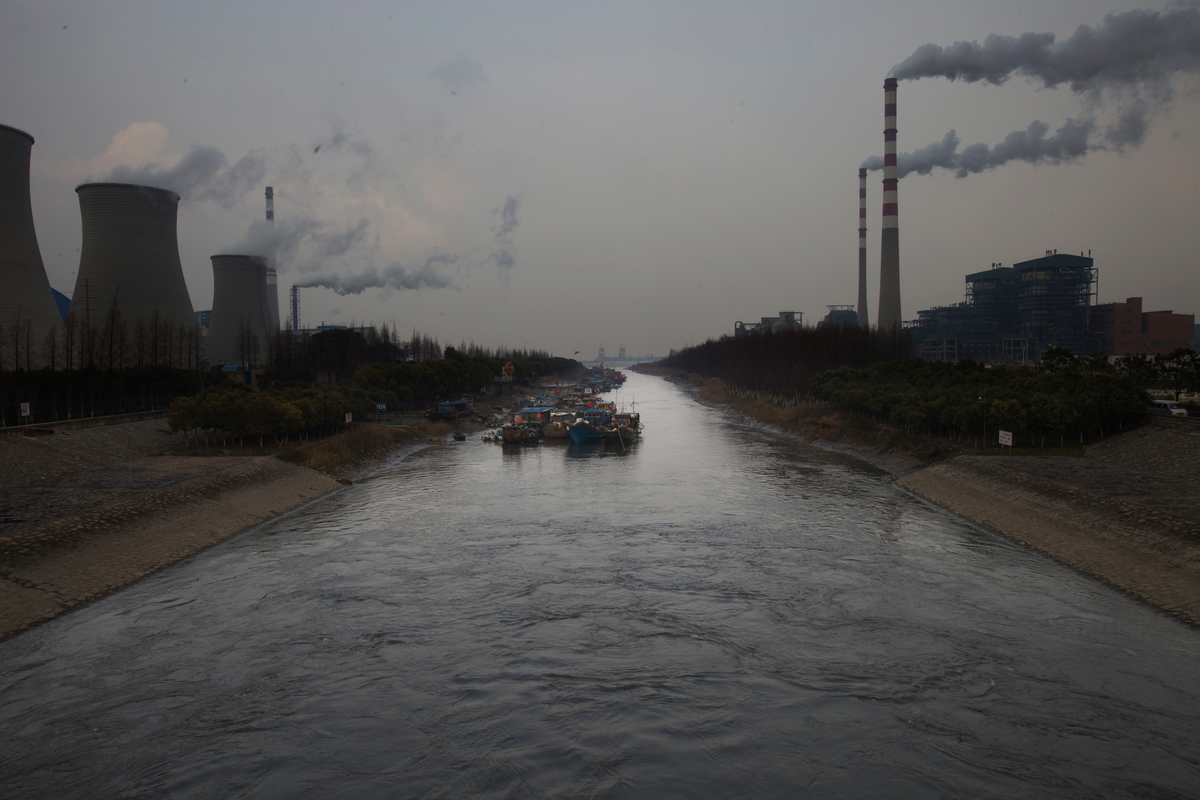
How the Coal Industry is Aggravating the Global Water Crisis
In its Global Risks Report 2015, the World Economic Forum stated “water security is one of the most tangible and fastest-growing social, political and economic challenges faced today.”1 Out of all industrial production, the coal industry represents one of the greatest demands on fresh water resources. The entire coal supply chain, including extraction, washing, coal-fired…
-
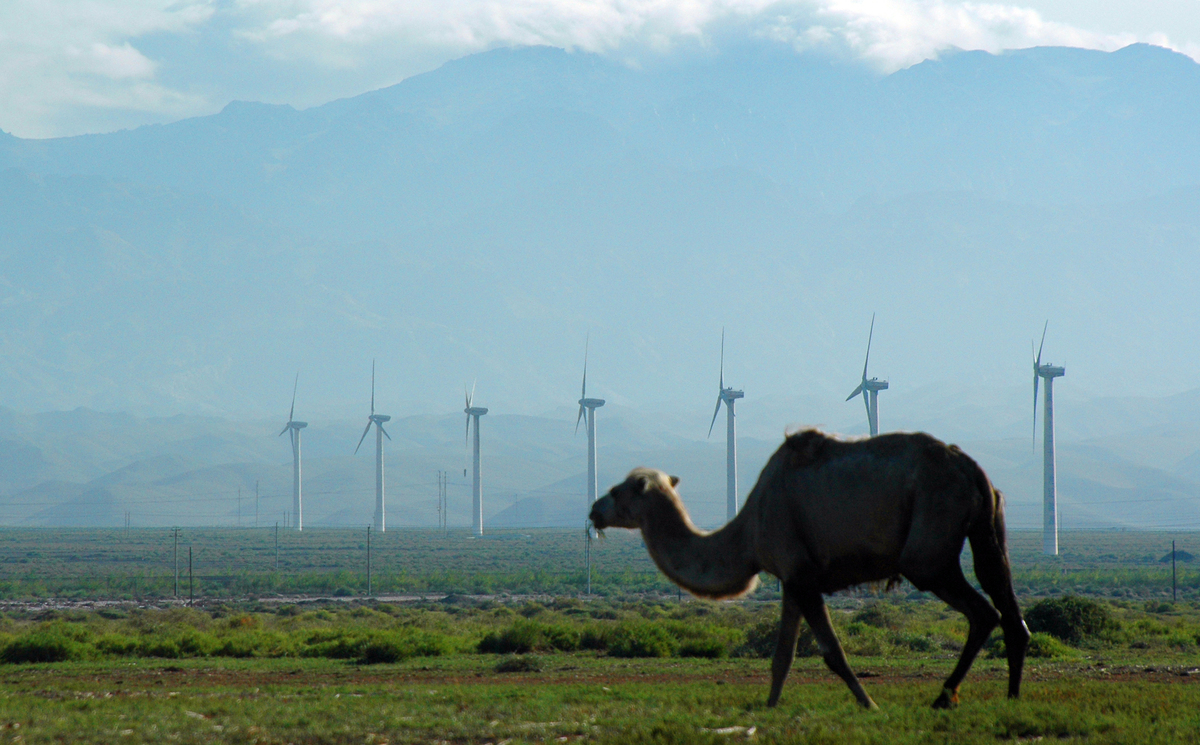
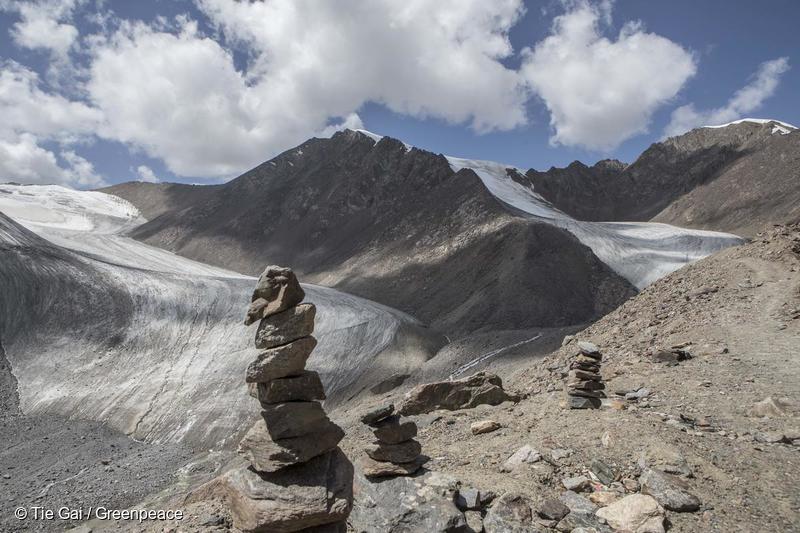
China’s 13th Five Year Plan hints at stronger climate ambition – Greenpeace
Beijing, 17 March 2016 - China's 13th Five Year Plan released today could indicate the world's largest carbon emitter will ramp its climate targets up within the next five years, just weeks after a recent paper also suggested that China’s emission may already have peaked.
-
Greenpeace: In spite of China’s overcapacity crisis, 210 new coal fired power plants received environmental permits in 2015
Beijing, 2 March, 2016 – An updated Greenpeace East Asia report has found that in 2015 a total of 210 new coal fired power plants were granted environmental permits, in spite of the sector’s severe overcapacity problem. Moreover, the rate at which these redundant power plants are being approved by provincial governments was dramatically higher…