The mining sector has become one of the pillars of the Indonesian economy. It contributes to Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and job creation. However, these economic gains are overshadowed by even greater detrimental effects on local communities and the environment.
The villages with mining as their main sector increased from 0.57% in 2018 to 0.71% in 2021, illustrating the rural economy’s higher dependence on the mining sector. However, these villages often face major challenges. This report reveals that villages that depend on the mining sector tend to have lower access to education than villages that focus on other sectors. There are fewer formal schools and other educational facilities in these villages, including a lack of secondary education as well as community training centers.
In addition, although the mining sector can drive economic development through job creation and export revenue. The villages surrounding the mining area often face difficulties in accessing basic services such as clean water and health facilities. These limitations directly impact the quality of life of local residents, with poorer access to health services and infrastructure.
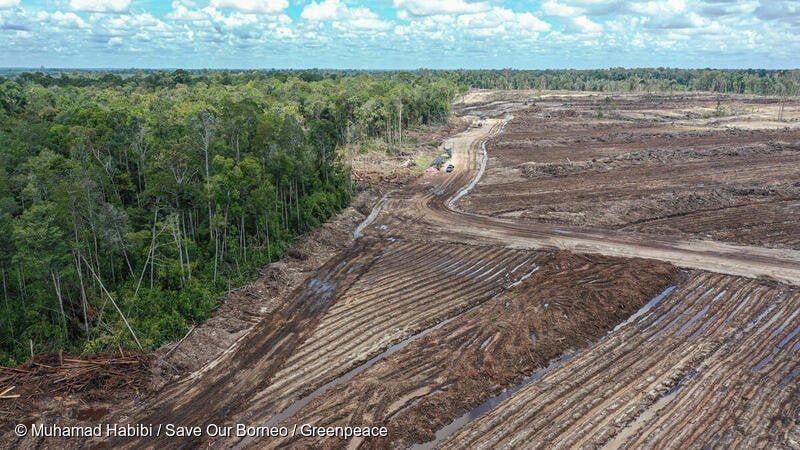
Mining poses a huge pressure to the environment. Mining villages tend to experience higher water, soil, and air pollution levels than other villages. Mining activities cause serious damage to local ecosystems, including deforestation and contamination of water sources. Furthermore, it threatens the health and livelihoods of local residents. This report highlights cases of extreme environmental pollution and degradation in various regions of Indonesia due to mining activities.
The health of the villagers living around the mines is clearly heavily impacted. They have limited access to health facilities, such as hospitals and community health centers, and often must travel long distances to obtain adequate medical services. Due to mining, there is a high risk of disease and health problems related to poor environmental conditions.
Villages that depend on mining also have limited access to communications technology and the internet. The lack of telecommunications infrastructure hampers their ability to participate in the digital economy, exacerbating isolation and hindering the development of small and micro businesses essential for economic diversification.